
Vitamin B12 – Effects, requirements, and intake explained
Vitamin B12 is a real power vitamin. Here you will learn why it is so important, how much you need per day, and what you need to know about its intake.
What exactly is vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 falls under the category of water-soluble B vitamins. Unlike most other vitamins in this group, it can be stored in the body for extended periods of time, primarily in the liver. As a result, it often takes months or even years for a deficiency to become apparent if too little is consumed through diet.
Since the body cannot produce vitamin B12 itself, it is important to regularly consume sufficient amounts through food.1
From a chemical perspective, vitamin B12 belongs to the group of compounds known as cobalamins. These compounds contain the trace element cobalt at the center of their structure, hence their name. Without cobalt, vitamin B12 would not be functional and would be unable to perform its tasks in important processes such as cell division and energy production.
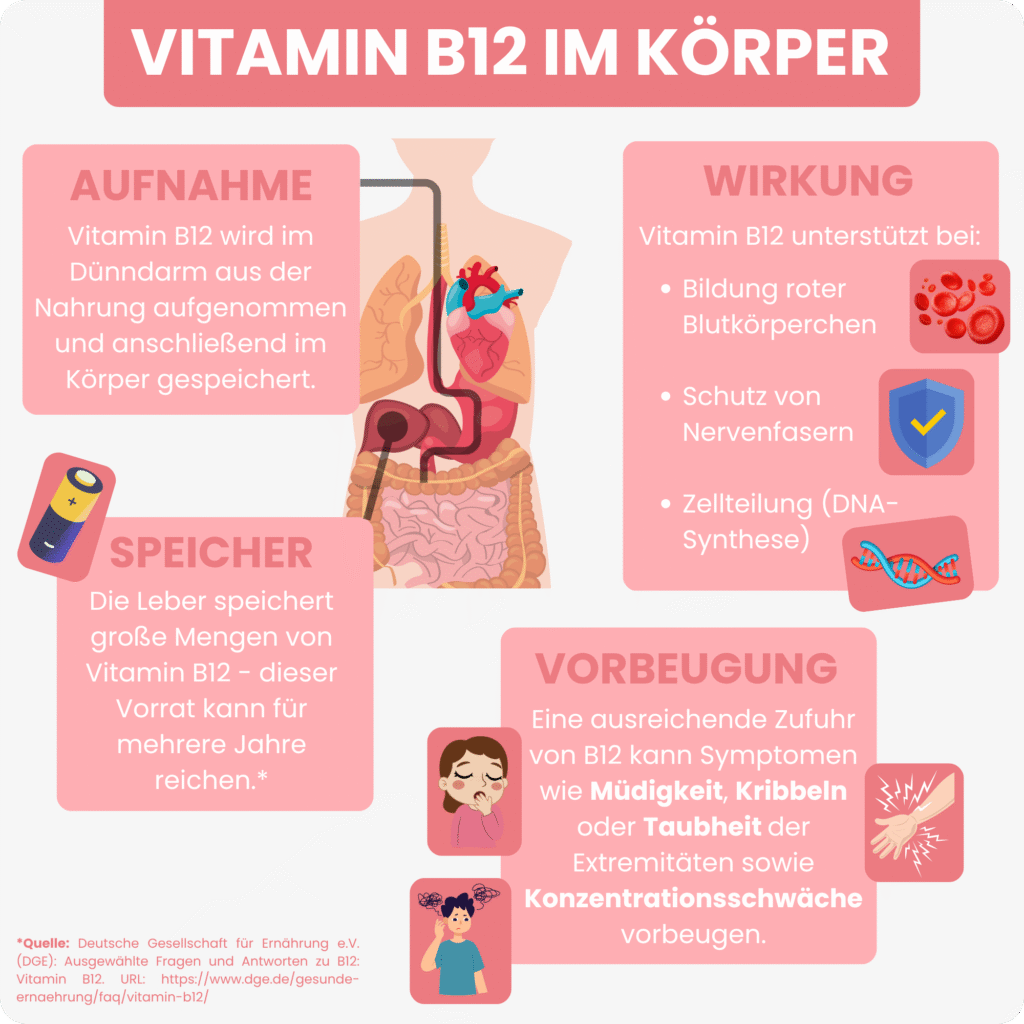
What is vitamin B12 good for?
Vitamin B12 performs many important tasks in your body. In particular, it supports the following functions:
Cell division, growth, and blood formation 1,3,4
🔬 Cell division
Cell division (mitosis) is the fundamental process by which one cell divides to form two new cells. This allows tissues to constantly renew themselves—whether in the skin, mucous membranes, or bone marrow.
→ Vitamin B12 is essential here because it is needed for DNA synthesis. Without sufficient B12, cells cannot divide correctly.
🌱 Growth
Growth means that the body forms new cells and existing tissues enlarge or regenerate. Growth therefore depends directly on functioning cell division.
→ If cell division proceeds smoothly, the body can grow, regenerate, and replace damaged structures.
🩸Blood formation
Blood formation (erythropoiesis) takes place in the bone marrow and is also based on cell division—specifically, the division of precursor cells that give rise to red blood cells (erythrocytes).
→ Vitamin B12, together with folic acid, plays a crucial role here: if there is a deficiency, the cells cannot divide properly, resulting in oversized, immature blood cells. The lack of oxygen supply can lead to fatigue and paleness.
Neural health and brain function 5,6
🧩 Nervous system
The nervous system controls almost all of your body’s functions—from movement and sensory perception to thoughts and emotions. In order for nerve impulses to be transmitted smoothly, nerve cells need a protective insulating layer called the myelin sheath.
→ Vitamin B12 is involved in the formation and maintenance of this myelin layer. If it is lacking, nerve impulses can only be transmitted slowly or incorrectly. This can manifest itself in tingling, numbness, or concentration problems.
🧠 Brain function
Vitamin B12 also plays an important role in the brain: it is involved in the production of certain messenger substances (neurotransmitters) that are important for mood, memory, and thought processes.
→ A good supply of vitamin B12 supports your mental performance and can help prevent poor concentration and mental fatigue. In the long term, it also protects the health of your nervous system.
Metabolism and energy balance 7,8
⚡ Metabolism
The nervous system controls almost all of your body’s functions—from movement and sensory perception to thoughts and emotions. In order for nerve impulses to be transmitted smoothly, nerve cells need a protective insulating layer called the myelin sheath.
→ Vitamin B12 is involved in the formation and maintenance of this myelin layer. If it is lacking, nerve impulses can only be transmitted slowly or incorrectly. This can manifest itself in tingling, numbness, or concentration problems.
🧠 Brain function
Vitamin B12 also plays an important role in the brain: it is involved in the production of certain messenger substances (neurotransmitters) that are important for mood, memory, and thought processes.
→ A good supply of vitamin B12 supports your mental performance and can help prevent poor concentration and mental fatigue. In the long term, it also protects the health of your nervous system.
Homocysteine metabolism and detoxification 9
🧬 Homocysteine metabolism
Homocysteine is an amino acid that is produced in the body as an intermediate product. Excessively high homocysteine levels can put strain on the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
→ Vitamin B12, together with folic acid and vitamin B6, plays a crucial role in converting homocysteine into methionine. This keeps the levels in your blood balanced and allows your metabolism to function smoothly.
♻️ Detoxification
By regulating homocysteine levels, vitamin B12 indirectly supports detoxification in your body. It helps to neutralize and eliminate harmful metabolic byproducts.
→ A good supply of vitamin B12 therefore helps your body to efficiently break down harmful metabolic products and keeps your cells healthy.
If you have a vitamin B12 deficiency, your body cannot reach its full potential.
If you have a vitamin B12 deficiency, your body cannot reach its full potential.

Für Veganer und Vegetarier
Vibe® 1 mg tablets
(contains 1.000 μg)
- high-dose vitamin B12
- certified vegan
- easy intake
How much vitamin B12 do you need per day?
Your body needs a certain amount of vitamin B12 every day to optimally support key bodily functions. The German Nutrition Society (DGE) provides recommendations on how much this should be each day.
Here you can see the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 for adults:
adults
4 µg

The requirements are particularly important for women at certain stages of life. The following table shows the recommended vitamin B12 levels for pregnant and breastfeeding women:10
pregnant women
4,5 µg
breastfeeding women
5,5 µg
The exact amount may vary slightly depending on age, lifestyle, and metabolism. People with certain health conditions, such as pernicious anemia, usually require specific medical treatment with vitamin B12 supplements.
Vibe® 1 mg tablets (equivalent to 1,000 μg) is a medicine for the long-term treatment of anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia) after blood levels have been stabilized following treatment with vitamin B12 injections.
The body's absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal-based foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products, where it is bound to proteins. In order for your body to absorb the vitamin, it must first be released from these proteins.
The absorption of vitamin B12 occurs in several steps:11
- Released in the stomach: In the stomach, stomach acid separates vitamin B12 from dietary proteins. At the same time, B12 immediately binds to a special transport protein. In addition, another protein is formed in the stomach, known as intrinsic factor, which later plays a crucial role in protecting and transporting B12.
- Transport to the small intestine: Vitamin B12 is transferred from the transport protein to the intrinsic factor. This complex protects the vitamin as it passes through the small intestine. At the end of the small intestine, vitamin B12 is actively absorbed.
- Transport to the bloodstream and body cells: From the small intestine, it enters the bloodstream, travels to the body’s cells, and is partially stored in the liver.
A major advantage
Your body can store vitamin B12 in the liver—sometimes for several years.10 This allows supply gaps to be compensated for over a certain period of time.
However, absorption does not depend solely on the amount consumed. Absorption capacity can be influenced by age, certain medications, or illnesses. One well-known cause is pernicious anemia. In this condition, the body does not produce enough intrinsic factor, a protein that is produced in the stomach and is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine. So even if sufficient B12 is absorbed through food, the body cannot utilize it properly in this case.
In such cases, medically prescribed treatment with vitamin B12 medications, such as Vibe® 1 mg film-coated tablets (equivalent to 1,000 μg), may be necessary. This preparation is used in adults for the long-term treatment of anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia) after blood values have been stabilized by injections.
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu Vitamin B12
What is vitamin B12 good for?
Vitamin B12 contributes to normal energy metabolism, supports normal nervous system function, supports normal psychological function, and helps reduce tiredness and fatigue.10
How much vitamin B12 do I need per day?
According to the German Nutrition Society (DGE), an adult needs around 4 µg of vitamin B12 per day, while pregnant women need 4.5 µg and breastfeeding women as much as 5.5 µg.10 Individual requirements may vary depending on age, lifestyle, and metabolism.
How can I meet my daily vitamin B12 requirement?
You can get vitamin B12 from certain foods (such as meat, fish, eggs, or dairy products).10 If you have a deficiency, supplements such as Vibe® 1 mg tablets (equivalent to 1,000 μg) can help. This is a supplement for the long-term treatment of anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia) after blood levels have been brought back to normal through treatment with vitamin B12 injections.
You may also be interested in

Vibe® 1 mg tablets provide your body with a targeted high dose of vitamin B12 – certified vegan, scientifically proven, and developed in Germany.

When your body needs more
Learn how high doses of vitamin B12 work, when they are necessary, and how they can be administered.

Are you getting enough vitamin B12?
Fatigue, concentration problems, or tingling in your fingers? What could be behind a vitamin B12 deficiency.
1 Rzepka, Zuzanna, u. a. „Response of Human Glioblastoma Cells to Vitamin B12 Deficiency: A Study Using the Non-Toxic Cobalamin Antagonist“. Biology, Bd. 10, Nr. 1, 2021, S. 69, doi:10.3390/biology10010069.
2 Batyrova, Gulnara. „The role of cobalt in human health: A brief overview“. West Kazakhstan Medical Journal, 2024, doi:10.18502/wkmj.v66i1.15599.
3 Strand, Tor A., u. a. „Vitamin B-12, Folic Acid, and Growth in 6- to 30-Month-Old Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial“. Pediatrics, Bd. 135, Nr. 4, 2015, S. e918-26, doi:10.1542/peds.2014-1848.
4 Krzywański, Jarosław, u. a. „Vitamin B12 Status and Optimal Range for Hemoglobin Formation in Elite Athletes“. Nutrients, Bd. 12, Nr. 4, 2020, S. 1038, doi:10.3390/nu12041038.
5 Centro Universitário FMABC – Faculdade de Medicina do ABC, Santo Andre, SP, Brazil, u. a. „Effects of vitamin B12 deficiency on the Central Nervous System“. Journal of Pathology Research Reviews & Reports, 2022, S. 1–4, doi:10.47363/jpr/2022(4)139.
6 Wu, Fangfang, u. a. „Vitamin B12 Enhances Nerve Repair and Improves Functional Recovery after Traumatic Brain Injury by Inhibiting ER Stress-Induced Neuron Injury“. Frontiers in Pharmacology, Bd. 10, 2019, S. 406, doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00406.
7 Ge, Yong, u. a. „Vitamin B12 Regulates the Transcriptional, Metabolic, and Epigenetic Programing in Human Ileal Epithelial Cells“. Nutrients, Bd. 14, Nr. 14, 2022, S. 2825, doi:10.3390/nu14142825.
8 Tardy, Anne-Laure, u. a. „Vitamins and Minerals for Energy, Fatigue and Cognition: A Narrative Review of the Biochemical and Clinical Evidence“. Nutrients, Bd. 12, Nr. 1, 2020, S. 228, doi:10.3390/nu12010228.
9 McCaddon, Andrew, und Joshua W. Miller. „Homocysteine-a Retrospective and Prospective Appraisal“. Frontiers in Nutrition, Bd. 10, 2023, S. 1179807, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1179807.
10 „Vitamin B₁₂“. DGE, www.dge.de/gesunde-ernaehrung/faq/vitamin-b12/. Zugegriffen 17. Oktober 2025.
11 Brito, Alex, u. a. „Methods to Assess Vitamin B12 Bioavailability and Technologies to Enhance Its Absorption“. Nutrition Reviews, Bd. 76, Nr. 10, 2018, S. 778–792, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy026.


